Ryder System, Inc., a leader in supply chain, dedicated transportation, and fleet management solutions, announces the establishment of Baton, A Ryder Technology Lab, based in Silicon Valley. Baton’s mission is to pioneer a suite of groundbreaking customer-facing technologies designed to revolutionize how Ryder’s customers interact with their transportation and supply chain networks. These technologies will digitize and optimize networks at a level not currently available in the industry and will prepare Ryder for the coming artificial intelligence wave.
“The establishment of a Silicon Valley-based technology lab is a natural evolution for Ryder, as we build on the $1.3 billion in strategic investments we’ve made over the past five years to develop, acquire, and invest in innovative technologies, products, and services that help make our customers’ logistics networks more efficient and resilient,” says Karen Jones, CMO and head of new product development for Ryder. “To build on that success, it’s paramount we continue to invest in recruiting the brightest technology minds out there and provide them with a startup environment where they have the space and freedom to create, along with the resources of a $12 billion company.”
Leading Ryder’s innovation lab are Andrew Berberick and Nate Robert, co-chief product and technology officers for Ryder. The two founded San Francisco-based startup Baton, which was known for the development of a proprietary logistics technology focused on optimizing transportation networks. Ryder initially invested in Baton’s Series A funding round and then acquired the startup last year.
“What piqued our interest in Ryder then, and what keeps us excited today, is the fact that it’s the only fully integrated port-to-door logistics provider in North America managing the complex supply chains of many of the world’s biggest and best-known brands. That gives Ryder tremendous perspective and reach, and as engineers, it provides us with the unique opportunity to tackle some of the largest and most daunting problems in the industry today, while preparing Ryder and its customers for the coming AI wave,” says Berberick.
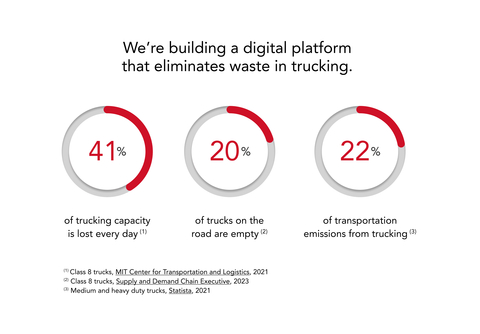
Baton’s first challenge is to create a first-of-its-kind, AI-powered digital platform and optimization engine that facilitates a new, integrated approach to managing transportation networks for customers where seasonality and fluctuating demand inhibit the continuous use of resources.
“There is a massive amount of waste when supply chains do not communicate. We believe we can change that and bring deep transformation to an entire sector,” says Robert. “That’s why we’re now actively recruiting talented technologists from some of Silicon Valley’s most respected technology firms to help solve some of the most complex problems plaguing the nearly $2.5 trillion North American transportation and logistics industry. We’re looking for engineers excited by the challenge and who want the autonomy and nimbleness of a startup environment but with the power, reach, and stability of a highly respected industry titan.”
Berberick holds a bachelor’s and master’s degree from Stanford University and worked for Google, Accenture, and Mindtribe; Robert holds a bachelor’s degree from MIT and master’s degree from Stanford University and worked for BuildZoom and Bain & Company, prior to cofounding Baton. Other key members of the Baton technology lab bring experience from Apple, Meta, OpenAI, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Tesla, Loadsmart, Kinema Systems (acquired by Boston Dynamics), PlayStation, Zynga, and LinkedIn.