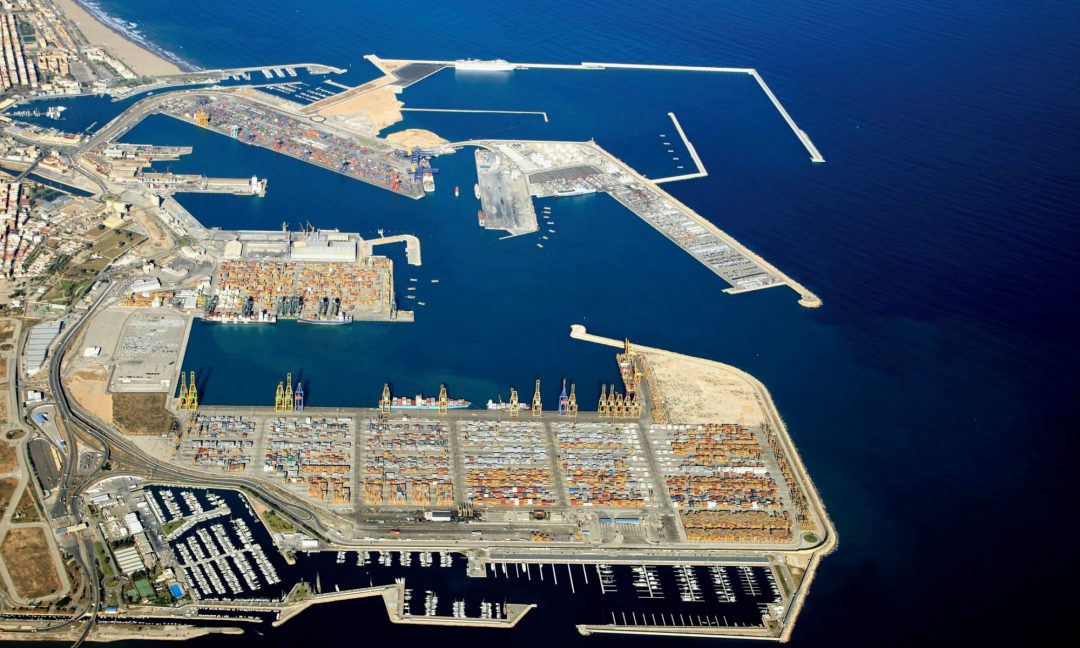
The use of hydrogen in the Port of Valencia to reduce the environmental impact of machinery operations in a terminal that operates 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, will make Valenciaport the first port in Europe to incorporate this energy in this activity. A project that has been recognised by different organisations and which the European Commission has selected as a strategic initiative for the decarbonisation of maritime transport, and which the Port Authority of Valencia has presented at the European Hydrogen Week 2021, as an example of the maritime sector’s commitment to decarbonisation and the fight against climate change.
The head of Strategic Planning and Innovation of the PAV, Juan Manuel Díez, explained that “Valenciaport is working on the European H2PORTS project to apply the use of hydrogen in terminal machinery. To this end, prototypes are being prepared that will be used to test this technology and its contribution to the decarbonisation of the logistics and maritime sector”. Díez participated in the session “Ports as European and global enablers” together with Jacques Vandermeiren, CEO of Antwerp Port Authority; Tudor Constantinescu, Principal Adviser DG Energy, European Commission Panellists; Reggy Vermeulen, CEO of Port Duqm, Oman; Bart Biebuyck, Executive Director, FCH JU; RADM Virgil Chițac, Mayor of Constanța (TBC); and Kadri Simson, European Commissioner for Energy.
The H2Ports project is an Action aligned with the needs and objectives of the European Commission and the port industry. The aim is to provide efficient solutions to facilitate a rapid evolution towards a low-carbon and zero-emission sector. “It is a project that we are developing in the Port of Valencia that will allow us to apply this technology in our facilities. At the same time, it will serve to implement this energy in the supply chain as the ports have to be the allies of the logistics community in the reduction of emissions and decarbonisation”, said the head of Strategic Planning and Innovation of the PAV.
The Port of Valencia will install a “hydrogen station” or green hydrogen supply station at the beginning of 2022. The station will be mobile and will provide the necessary fuel, in the appropriate conditions and quantities to guarantee the continuous working cycles of the equipment forming part of the H2Ports project. The first of this equipment will be the machine or prototype of the Reach Stacker vehicle or “container stacker” which will be powered by this energy and which will be tested at MSC Terminal Valencia. The second piece of equipment to be serviced by the hydrogen plant will be a 4×4 tractor unit equipped with a fuel cell stack for testing in loading/unloading operations at Valencia Terminal Europa of the Grimaldi Group.
During his intervention at the EHW, Juan Manuel Díez, indicated that “it is important that we explain our experience to other ports that can act as promoters of these clean energies”. In this sense, the head of Strategic Planning and Innovation of the PAV pointed out that “Valenciaport is very active in local and regional initiatives that promote this collaboration, but also at European and world level, which is why we are part of the Clean Hydrogen Alliance and the Global Ports Hydrogen Coalition. In addition, within the framework of the H2 Port project, we have created an advisory group open to more than 65 members and 30 ports from all over the world in which we are working on the construction of the hydrogen value chain for ports”.
“This type of project – he continued – is part of our commitment to our cities and area of influence to promote green energies and the reduction of emissions. In addition, we are positioning the Port as an energy hub with the use of hydrogen, wind or photovoltaic energy to provide solutions applicable to other sectors”.
H2PORTS Project
The European project “H2PORTS – Implementing Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Technologies in Ports” is coordinated by the Valenciaport Foundation and the PAV, and financed by the Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Joint Undertaking (FCH JU) programme. H2Ports will involve a total investment of 4 million euros and, in addition to the Valenciaport Foundation and the Port Authority of Valencia, the National Hydrogen Centre, and the companies MSC Terminal Valencia, Grimaldi Group, Hyster-Yale, Atena Distretto Alta Tecnologia Energia Ambiente, Ballard Power Systems Europe and Enagás.
The PAV’s initiative for the use of hydrogen in its facilities has already been recognised by the Spanish Government within the framework of the Hydrogen Roadmap and forms part of H2VLC Valencia Hydrogen Valley, in which the City Council of Valencia, the Generalitat Valenciana and the Universitat Politècnica de València also participate.
Hydrogen Strategy
The Europena Hydrogen Week (EHW 2021) is an event that brings together European industry, policy makers, government representatives and the research community to discuss the growing potential of hydrogen in the coming years. EHW 2021 has addressed the opportunities associated with the production and use of hydrogen and hydrogen-based fuels in different sectors of the economy and how hydrogen will play a key role in the European Green Deal. Valenciaport participated in the conference entitled “European Hydrogen Strategy: Energy, Transport and Standardisation Policies”.