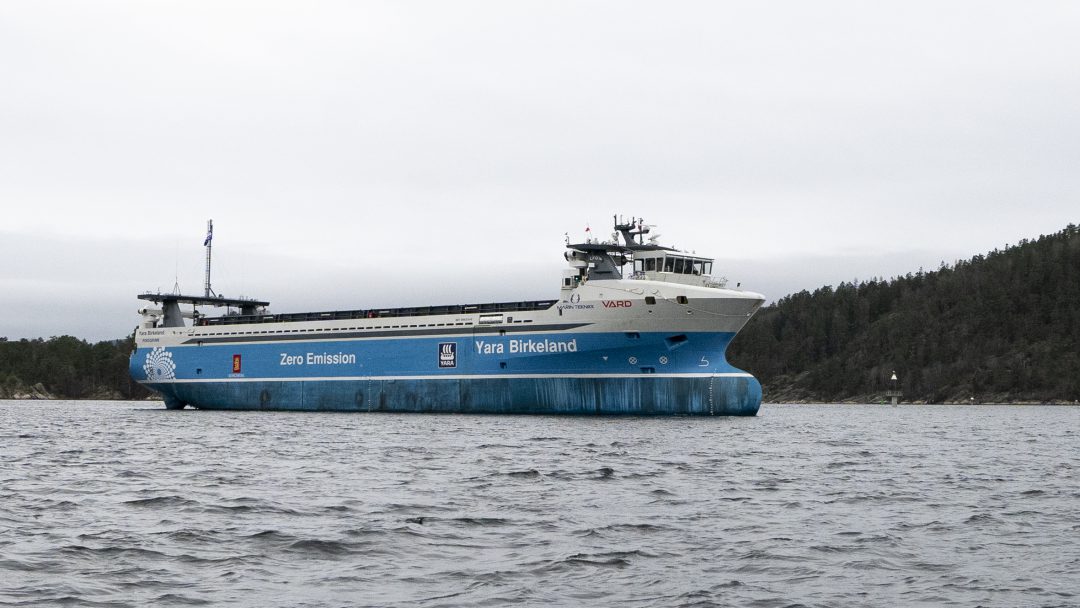
The Yara Birkeland, the world’s first autonomous and fully electric container ship, will soon commence commercial operations while beginning a two-year test period, prior to entering full autonomous operation on a route off the coast of Norway. It is fully powered by a Leclanché high-energy lithium-ion battery system.
The emission-free and safe energy supply is provided by a 6.7 MWh battery system with integrated liquid cooling to ensure optimum operating temperature. The Leclanché Marine Rack System ensures optimum temperature control of the cells and their permanently reliable operation over a service life of at least 10 years. In addition, the MRS offers state-of-the-art protection against overheating and an integrated fire protection system specifically designed and certified for maritime requirements.
The Yara Birkeland has completed its maiden voyage to Oslo in mid-November and then sailed on to Porsgrunn, the southern Norwegian production site of Yara International a fertiliser manufacturer and the vessel owner.
Leclanché supplied a 6.7 MWh battery system (which represents the same energy as 130 Tesla Model 3 batteries) for the energy supply of the approximately 80 meters long and 15 meters wide container ship with a deadweight of 3,120 tonnes or 120 standard containers (TEU). This electrically powered “green vessel” will operate at a service speed of approximately 6 knots, with a maximum speed of 13 knots.
“Yara is constantly seeking opportunities to reduce its climate footprint and fulfil its main vision to responsibly feed the world. Embarking on a technical challenging project as Yara Birkeland together with our technology partner Kongsberg Maritime is as such a small endeavour in the large challenge we as one out of many industrial players are embarking. A zero-emission vessel to bring our product from production and out to the markets show that it is possible to make a positive contribution to the required change in the release of climate gases. A saying from one of Yara’s founders back in early 19th century is “where there is a will, there is a way”. Battery technology from Leclanché provides us with a battery driven vessel charged with electricity from the green hydroelectric power. This is a willful step in a green direction and an encouragement for others to also invest in future technologies”, said Jon Sletten, project owner, Yara Birkeland.
“We are very proud to be able to contribute to the success of this unique project. With our battery system for the Yara Birkeland, Leclanche contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to 40.000 container truck road journeys per year, not to mention road safety improvements, noise pollution reduction and increased logistics efficiencies,” said Anil Srivastava, chief executive officer of Leclanché. “The annual operating cost savings in both fuel and crew, estimated at up to 90%, makes autonomous and battery powered ships viable in international trade. Combined with new emerging technologies and the integration of alternative green fuels, including clean hydrogen, we will continue opening new possibilities for our customers, the industry and the planet.”
Lithium-ion battery system – made in Europe
The battery system of the Yara Birkeland, manufactured in Switzerland, is fitted with lithium-ion cells which are produced at Leclanché’s automated production facility in Willstätt, Germany and battery modules made in Switzerland. The high energy density cells combined with long life cycle of 8,000 @ 80% DoD, with operating temperature ranges from -20 to +55°C, are at the core of the battery system. This Leclanché Marine Rack System consists of 20 strings with 51 modules of 32 cells each, for a total of 32,640 cells. The battery system has built-in redundancy, with eight separate battery rooms: if multiple strings are emptied or stop working, the vessel can continue its operations.
When it comes to battery systems for marine applications, efficient protection against overheating is indispensable. To prevent a fire on the open sea, Leclanché specially developed the modular DNV-GL certified MRS. Each battery string contains gas and smoke detectors, redundant thermal monitoring and a cooling system to prevent overheating and thermal incidents. Should a thermal incident occur despite all this, the Fifi4Marine fire extinguishing system kicks in: based on environmentally friendly foam, it cools and extinguishes quickly and effectively.
Zero emissions thanks to battery drive
Once the test period is completed, the Yara Birkeland will navigate on a completely autonomous basis transporting containers products from Yara International’s production plant in Herøya to the port of Brevik. Yara International is pursuing a zero-emission strategy with the all-electric drive solution: the vessel’s operation will displace around 40,000 truck journeys per year and the associated NOx and CO2 emissions. It also reduces noise and air pollution while in port. The batteries are charged automatically with electricity from renewable sources.
“Leclanché’s marine rack system provides 30% higher energy density and up to a 230% greater life cycle than competitive systems – in addition to its reputation for having the safest battery system design,” said Guillaume Clement, VP e-Marine, Leclanché. “Thanks to Yara, the maritime industry has entered a new era where sustainable shipping is demonstrated as a viable solution for a very large range of ships and businesses.”
e-Marine at Leclanché
Sustainability is an important and serious business and cultural commitment for Leclanché. All of the Company’s products and its sustainable production methodologies allow it to make an important contribution to the e-mobility industry and the global energy transition to sustainability. Leclanché is one of the few European battery system suppliers that has its own cell production facilities and the complete know-how to produce high-quality lithium-ion cells — from electrochemistry to battery management software and an array of battery systems. The systems are used in stationary energy storage systems, trains, buses and ships, among others. The e-Marine sector is currently Leclanché’s fastest growing business segment. The company has already delivered battery systems for multiple ships with electric or hybrid propulsion systems with orders for many more. Among the projects successfully completed is “Ellen,” a passenger and vehicle ferry which has been operating in the Danish Baltic Sea since 2019 and is the longest range, all-electric ferry in daily operation.