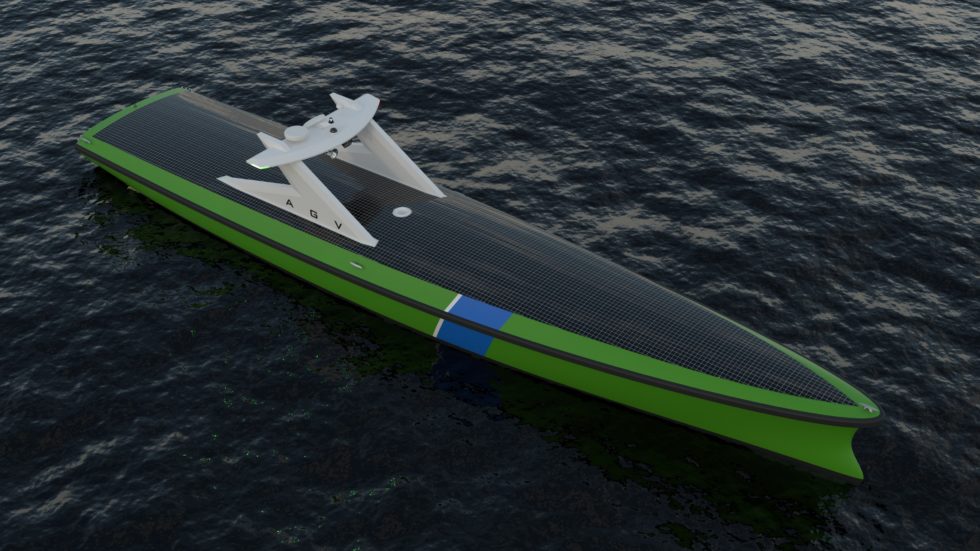
A consortium of maritime partners unveiled the concept design of an Autonomous Guard Vessel on Tuesday 7 July. C-Job Naval Architects, in collaboration with LISA Community, Seazip Offshore Service, Sea Machines, MARIN and eL-Tec Elektrotechnologie, created a modern design which will support the offshore industry by exploiting technology available today.
Modern autonomous design
The novel design is smaller and lighter than most current guard vessels used to protect offshore operations and boasts sustainable solutions as well as exploiting the benefits of autonomous shipping. In addition, the Autonomous Guard Vessel (AGV) is set to operate more efficiently as well as require lower operating costs due to no crew being required.
This clean and lean concept to replace conventional guard vessels came to life in a project group facilitated by LISA, a community for maritime professionals. The project group resulted in a consortium, which includes C-Job Naval Architects, SeaZip Offshore Service, Sea Machines and recently joined by MARIN and eL-Tec elektrotechniek BV. Their combined industry knowledge created this viable, innovative, and sustainable alternative which benefits both wind asset owners and guard vessel operators.
Offshore structures surveillance
The Autonomous Guard Vessel is specifically designed for surveillance of offshore structures throughout their life cycle, ranging from wind farms to substation platforms and cable routes. With any area that needs to be secured, the AGV can continuously monitor nearby marine traffic visually as well as via radar and AIS data. With any vessel that approaches the area, measures will be taken to secure the area in order to avoid collisions and damage to the offshore infrastructure. An intruding vessel can be communicated with and will receive information on how to safely navigate the area as well as being physically escorted away from the site by the Autonomous Guard Vessel. Additionally, the encounter will be recorded to provide video footage in case of any violation or accident.
Pelle de Jong, Founding Partner LISA, explains “Guard vessels perform an essential job, however, it is not the most exciting one for crew. Combined with the fact that conventional guard vessels are mostly outdated and thus aren’t necessarily the most comfortable let alone sustainable, it can be difficult to find well-trained crew willing to do the job.
“The group set out to improve upon the overall process of securing an offshore area while incorporating sustainable solutions and reducing overall cost. By utilizing the knowledge we have as a group as well as the technology already available, we succeeded in creating a design which does this and more.”
Sustainable features
Thanks to incorporating state-of-the-art technology, the Autonomous Guard Vessel does not require crew onboard the vessel. Therefore, accommodations can be eliminated in the design, meaning the ship will be considerably smaller than existing guard vessels. The smaller size creates a number of opportunities, such as using batteries thanks to reduced propulsion requirements. Additionally, the reduced power and lack of onboard crew leads to lower operational costs.
Sustainability is key to ensure both the viability and durability of the design. Rolph Hijdra, Autonomous Research Lead at C-Job Naval Architects, says “We are pleased we were able to develop a battery-powered design, ensuring the Autonomous Guard Vessel is free of harmful emissions. Additionally, the ship has solar panels across the top which allows for the continuation of navigation and communications in case the batteries run out of power.
“Contrary to current guard vessels, the AGV will continue to be operational even with rough sea conditions and have minimal underwater noise owing to the smaller size, reduced propulsion requirements and absence of a diesel engine.”
Multiple AGVs onsite
The Autonomous Guard Vessel will recharge its batteries via a charging station. The charging station can be moored independently or connected to existing equipment onsite. Depending on the situation, charging could either be via a cable connection to the on-site equipment such as an offshore transformer platform or locally generated using renewable fuels.
The consortium envisions an offshore site will need a number of Autonomous Guard Vessels, which can take turns in monitoring the area and recharging. Harm Mulder, Operations Manager at SeaZip Offshore Service, says “The Autonomous Guard Vessels will be constantly patrolling the area and take turns recharging. One fully charged AGV will remain on stand-by supporting operations if a situation arises. For example, when an intrusion is detected – one of the AGVs will monitor, warn, and escort the intruding ship to safety, while the others continue normal operations. Alternatively, it could take over from a monitoring vessel in case the battery runs out of power.”
Human intervention via Command Center
While the consortium continues to work on the Autonomous Guard Vessel design, they have considered human intervention for the unmanned vessel. Conventional guard vessels patrolling offshore structures, from installation through to decommissioning, have few incidents that require intervention from those onboard the vessel. For those exceptional circumstances the Autonomous Guard Vessel, if human intervention would be required, will be connected to a Command Center which could control the AGV remotely to ensure correct action is taken. In addition, all data collected by the AGV will be send to the Command Center. This can be a standalone on a mother ship or a shore-based station.
Smart vessel technology for niche market segments
Frank Relou, Business Development Manager at Sea Machines, says “Smart vessel technology will have the most significant initial impact on small workboats, such as this guard vessel. The development of autonomous technology for vessel operations are occurring on an international level but namely in niche segments, such as the guard vessel and other examples, currently operating in (with supervised autonomy), marine survey, fire, patrol, aquaculture and offshore wind operations.”